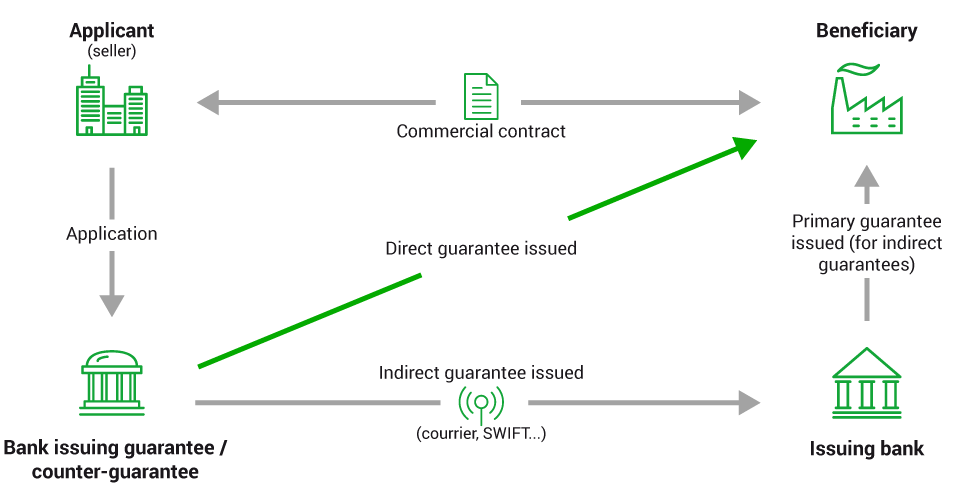
- BCV makes a commitment to a creditor, such as a supplier, at your request and on your behalf (or on behalf of a third party) to pay a certain amount provided that the conditions set out in the guarantee are met.
- By using BCV for this type of transaction, you have the backing of a bank that is recognized for its solidity – all at a low fee for you.
- Our bank guarantees are only available to clients residing in Switzerland.
By continuing to use this website, you agree to our use of cookies to offer you personalized services and content, calculate statistics on website visits, and enable you to share content on social networks. Learn more.
Be on the lookout for scammers! Never share your log-in details, bank card numbers, or PIN codes. BCV will never ask you for this information. Always double-check your payment orders (payee’s name, amount). Never install remote access software on your devices. Learn more